Wat is bitcoin?

The world’s first widely-adopted cryptocurrency. With Bitcoin, people can securely and directly send each other digital money on the internet.
Bitcoin was created by Satoshi Nakamoto, a pseudonymous person or team who outlined the technology in a 2008 white paper. It’s an appealingly simple concept: bitcoin is digital money that allows for secure peer-to-peer transactions on the internet.
Unlike services like Venmo and PayPal, which rely on the traditional financial system for permission to transfer money and on existing debit/credit accounts, bitcoin is decentralized: any two people, anywhere in the world, can send bitcoin to each other without the involvement of a bank, government, or other institution.
Every transaction involving Bitcoin is tracked on the blockchain, which is similar to a bank’s ledger, or log of customers’ funds going in and out of the bank. In simple terms, it’s a record of every transaction ever made using bitcoin.
Unlike a bank’s ledger, the Bitcoin blockchain is distributed across the entire network. No company, country, or third party is in control of it; and anyone can become part of that network.
There will only ever be 21 million bitcoin. This is digital money that cannot be inflated or manipulated in any way.
It isn’t necessary to buy an entire bitcoin: you can buy just a fraction of one if that’s all you want or need.
Belangrijke vragen
Wat is BTC?
BTC is de afkorting van bitcoin.
Is bitcoin een crypto?
Ja, bitcoin is de eerste algemeen aanvaarde crypto, wat gewoon een andere naam is voor digitaal geld.
Is er een eenvoudige definitie voor bitcoin?
Bitcoin is een gedecentraliseerde digitale valuta die wordt gebruikt voor versleutelde, peer-to-peer transacties zonder dat er een centrale bank nodig is
Wat is de prijs van bitcoin?
De huidige prijs van bitcoin is te vinden op de website van Coinbase.
Zijn bitcoins een investeringskans?
Net als elk ander activum, kunt u winst maken door BTC tegen een lage prijs te kopen en tegen een hogere prijs te verkopen, of verlies maken in het omgekeerde scenario.
Wat was in het begin de prijs van bitcoin?
Eén BTC werd begin 2010 gewaardeerd op een fractie van een Amerikaanse cent. In het eerste kwartaal van 2011 was de waarde hoger dan een dollar. Eind 2017 schoot de waarde omhoog tot bijna $ 20.000 en Bitcoin bereikte uiteindelijk een piek van $ 64.899 in november 2021. U kunt hier de prijs van bitcoins volgen.

Bitcoin is een gedecentraliseerde digitale valuta die wordt gebruikt voor versleutelde, peer-to-peer transacties zonder dat er een centrale bank nodig is
What Is Bitcoin? by Coinbase CEO Brian Armstrong Buy your first Bitcoin Start with as little as $25 Get started
Bitcoin Basics
Since Bitcoin’s creation, thousands of new cryptocurrencies have been launched, but bitcoin (abbreviated as BTC) remains the largest by market capitalization and trading volume.
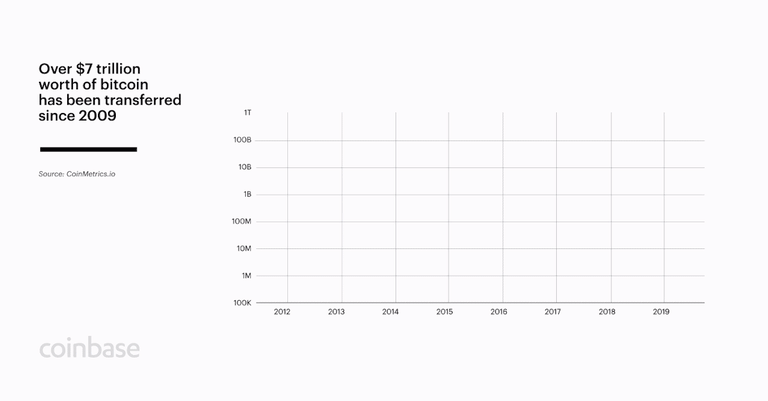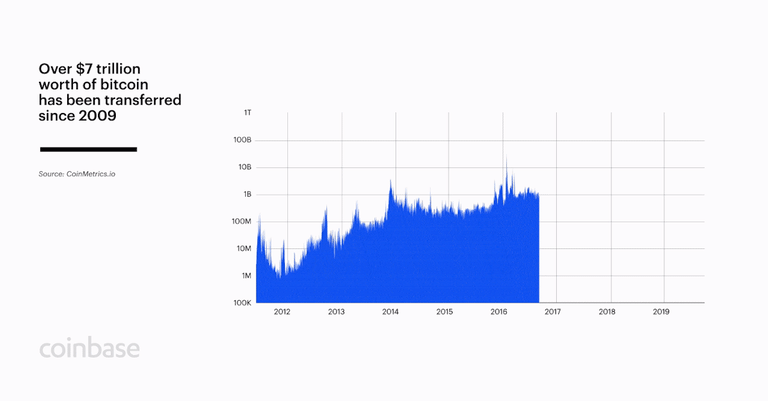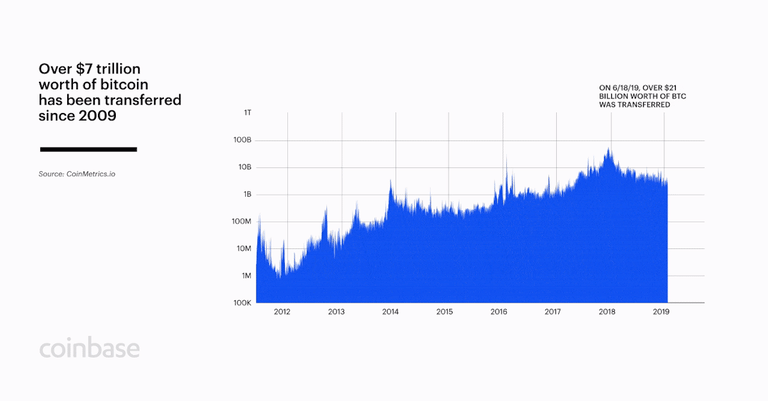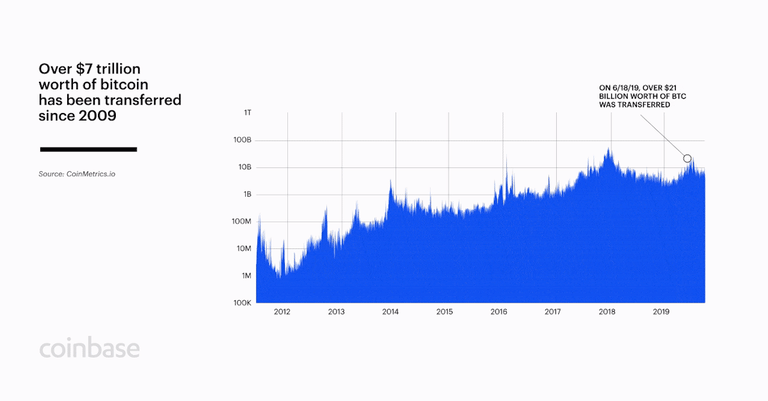
Depending on your goals, bitcoin can function as
- an investment vehicle
- a store of value similar to gold
- a way to transfer value around the world
- even just a way to explore an emerging technology
Bitcoin is a currency native to the Internet. Unlike government-issued currencies such as the dollar or euro, Bitcoin allows online transfers without a middleman such as a bank or payment processor. The removal of those gatekeepers creates a whole range of new possibilities, including the potential for money to move around the global internet more quickly and cheaply, and allowing individuals to have maximum control over their own assets.
Bitcoin is legal to use, hold, and trade, and can be spent on everything from travel to charitable donations. It’s accepted as payment by businesses including Microsoft and Expedia.
Is bitcoin money? It’s been used as a medium of exchange, a store of value, and a unit of account—which are all properties of money. Meanwhile, it only exists digitally; there is no physical version of it.
Who created Bitcoin?
To really grasp how bitcoin works, it helps to start at the beginning. The question of who created bitcoin is a fascinating one, because a decade after inventing the technology—and despite a lot of digging by journalists and members of the crypto community—its creator remains anonymous.
The principles behind Bitcoin first appeared in a white paper published online in late 2008 by a person or group going by the name Satoshi Nakamoto.
This paper wasn’t the first idea for digital money drawing on the fields of cryptography and computer science—in fact, the paper referred to earlier concepts—but it was a uniquely elegant solution to the problem of establishing trust between different online entities, where people may be hidden (like bitcoin’s own creator) by pseudonyms, or physically located on the other side of the planet.
Nakamoto devised a pair of intertwined concepts: the bitcoin private key and the blockchain ledger. When you hold bitcoin, you control it through a private key—a string of randomized numbers and letters that unlocks a virtual vault containing your purchase. Each private key is tracked on the virtual ledger called the blockchain.
When Bitcoin first appeared, it marked a major advance in computer science, because it solved a fundamental problem of commerce on the internet: how do you transfer value between two people without a trusted intermediary (like a bank) in the middle? By solving that problem, the invention of bitcoin has wide-ranging ramifications: As a currency designed for the internet, it allows for financial transactions that range across borders and around the globe without the involvement of banks, credit-card companies, lenders, or even governments. When any two people—wherever they might live—can send payments to each other without encountering those gatekeepers, it creates the potential for an open financial system that is more efficient, more free, and more innovative. That, in a nutshell, is bitcoin explained.
Bitcoin creates the potential for an open financial system that is more efficient, more free, and more innovative.
Zo werken bitcoins
In tegenstelling tot creditcardnetwerken zoals Visa en betalingsverwerkers zoals Paypal, is bitcoin geen eigendom van een persoon of bedrijf. Bitcoin is 's werelds eerste, volledig open betalingsnetwerk waaraan iedereen met een internetverbinding kan deelnemen. Bitcoin is ontworpen voor gebruik op internet en is voor de verwerking van transacties niet afhankelijk van banken of particuliere bedrijven.
Een van de belangrijkste onderdelen van Bitcoin is de blockchain, waarmee wordt bijgehouden wie wat bezit, vergelijkbaar met hoe een bank activa bijhoudt. Wat de blockchain van Bitcoin onderscheidt van het grootboek van een bank, is dat het gedecentraliseerd is. Dat betekent dat iedereen het kan bekijken en dat geen enkele entiteit het beheert.
Zo werkt het:
Gespecialiseerde computers die bekend staan als 'mining rigs' voeren de vergelijkingen uit die nodig zijn om een nieuwe transactie te verifiëren en vast te leggen. Vroeger was een typische desktop-pc krachtig genoeg voor deelname, waardoor vrijwel iedereen die nieuwsgierig was mining kon uitproberen. Tegenwoordig zijn de benodigde computers enorm groot, gespecialiseerd en vaak eigendom van bedrijven of grote aantallen individuen die hun resources bundelen. (In oktober 2019 was 12 biljoen keer meer rekenkracht nodig om één bitcoin te minen, dan toen Nakamoto dat in januari 2009 voor het eerst deed.)
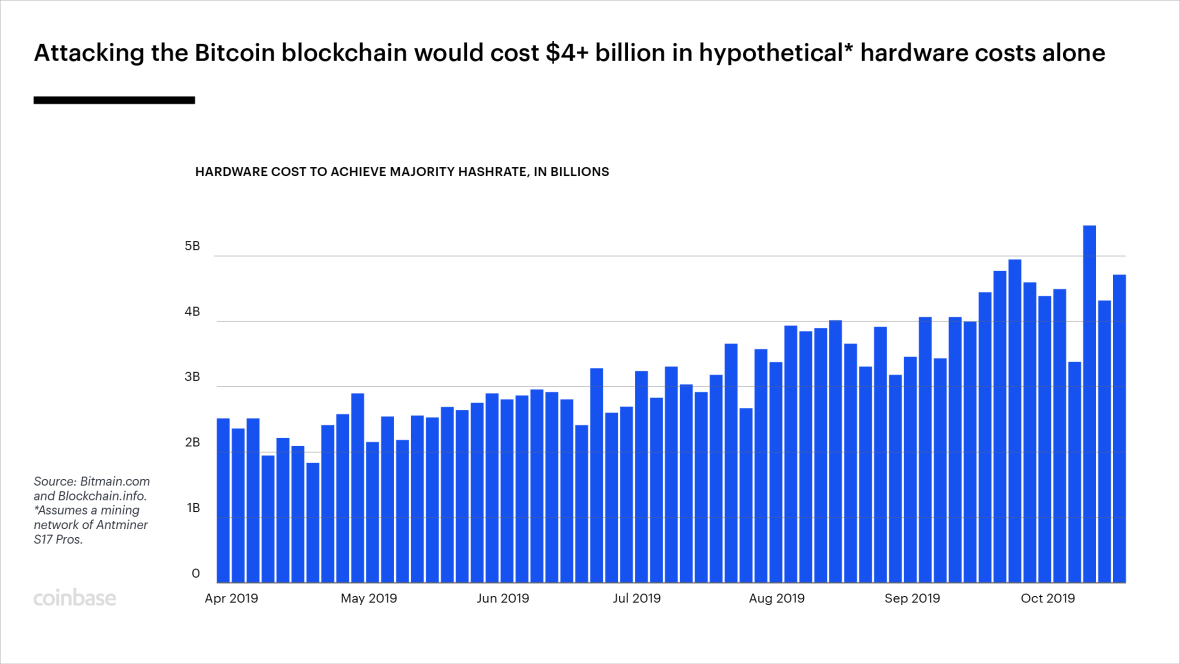
De collectieve rekenkracht van miners wordt gebruikt om de nauwkeurigheid van het steeds groter wordende grootboek te waarborgen. Bitcoin is onlosmakelijk verbonden met de blockchain; elke nieuwe bitcoin wordt erop geregistreerd, net als elke volgende transactie met alle bestaande coins.
Hoe motiveert het netwerk miners om deel te nemen aan het constante, cruciale onderhoud van de blockchain: het verifiëren van transacties? Het Bitcoin-netwerk houdt een continue loterij waarin alle mining rigs over de hele wereld alles op alles zetten om als eerste een wiskundig probleem op te lossen. Elke 10 minuten wordt een winnaar gevonden en de winnaar werkt het Bitcoin-grootboek bij met nieuwe geldige transacties. De prijs verandert in de loop van de tijd, maar in mei 2020 ging de beloning voor elke winnaar van deze loterij van 12,5 bitcoin per blok naar 6,25, en in 2024, met de halvering, daalde deze beloning verder van 6,25 naar 3,125 als een mechanisme om de schaarste te vergroten.
In het begin was een bitcoin eigenlijk waardeloos. Eind 2019 lag de koers op circa $ 7.500 en in november 2021 bereikte het een piek van $ 64.000. Naarmate de waarde van bitcoin stijgt, is het feit dat deze gemakkelijk deelbaar is (dus de mogelijkheid om een klein deel van één bitcoin te kopen) een belangrijk voordeel geworden . Eén bitcoin heeft momenteel acht cijfers achter de komma (100 miljoenste van één bitcoin); de bitcoincommunity noemt de kleinste eenheid een 'satoshi'.
Nakamoto heeft het netwerk zo opgezet dat er nooit meer dan 21 miljoen bitcoins zijn, wat voor schaarste zorgt. Per december 2023 waren er nog ongeveer 1,4 miljoen bitcoins beschikbaar om te worden gemined. Theoretisch vindt mining van de laatste blokken pas plaats in 2140.
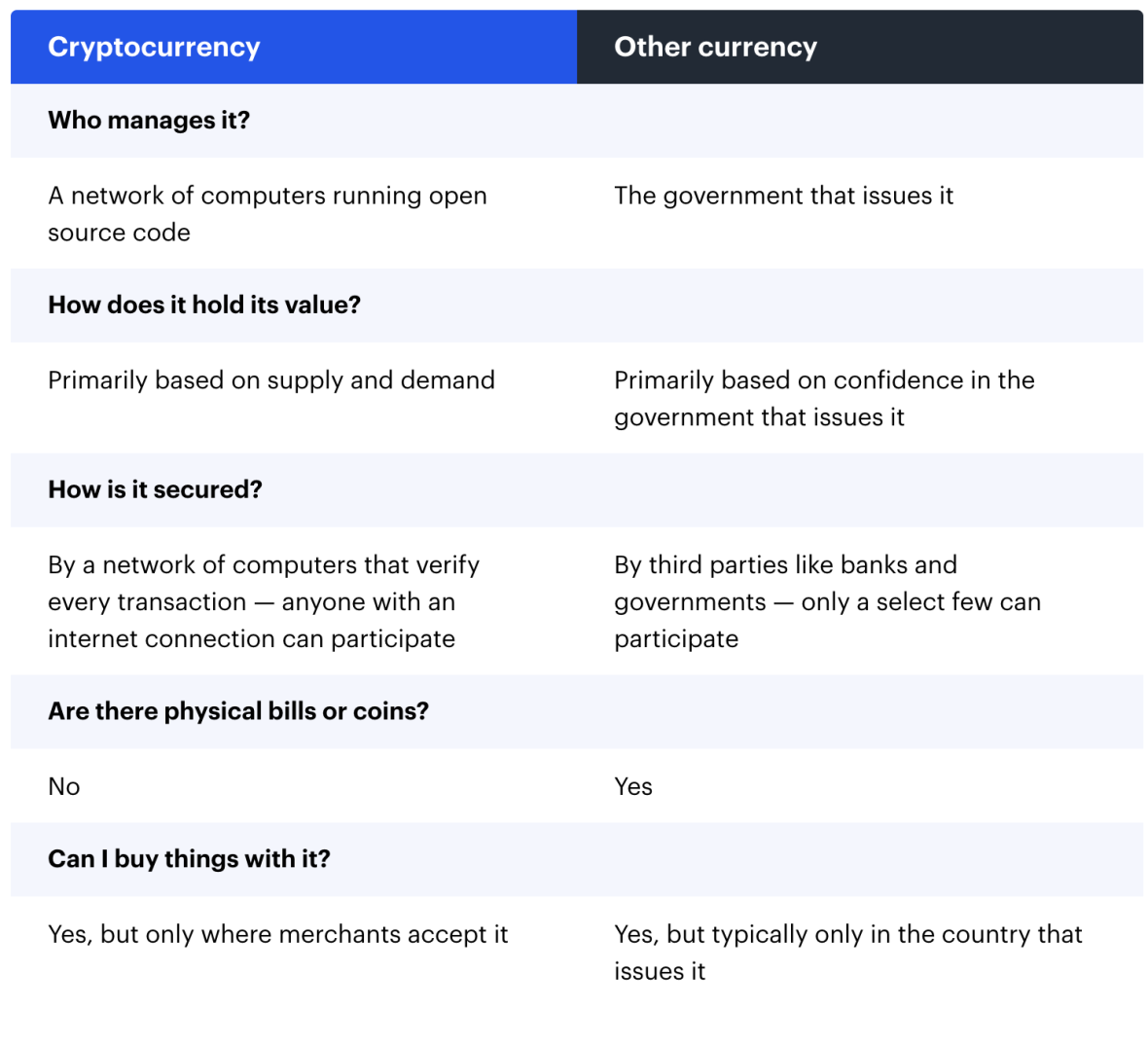
Cryptovaluta en traditionele valuta's delen enkele eigenschappen, zoals de manier waarop je ze kunt gebruiken om dingen te kopen of hoe je ze digitaal kunt overschrijven, maar ze zijn voor wat betreft andere interessante aspecten heel verschillend. Hier zijn wat belangrijke punten.
Bitcoin is 's werelds eerste, volledig open betalingsnetwerk waaraan iedereen met een internetverbinding kan deelnemen.
Key question
How does bitcoin have value?
Essentially the same way a traditional currency does – because it’s proven itself to be a viable and convenient way to store value, which means it can easily be traded for goods, services, or other assets. It’s scarce, secure, portable (compared to, say, gold), and easily divisible, allowing transactions of all sizes.
How to get Bitcoin
The easiest way to buy bitcoin is to purchase it through an online exchange like Coinbase. Coinbase makes it easy to buy, sell, send, receive, and store bitcoin without needing to hold it yourself using something called public and private keys.
How to buy bitcoin, with Coinbase CEO Brian Armstrong
However, if you choose to buy and store bitcoin outside of an online exchange, here’s how that works.
Each person who joins the bitcoin network is issued a public key, which is a long string of letters and numbers that you can think of like an email address, and a private key, which is equivalent to a password.
When you buy bitcoin—or send/receive it—you get a public key, which you can think of as a key that unlocks a virtual vault and gives you access to your money.
Anyone can send bitcoin to you via your public key, but only the holder of the private key can access the bitcoin in the “virtual vault” once it’s been sent.
There are many ways to store bitcoin both online and off. The simplest solution is a virtual wallet.
If you want to transfer money from your wallet to a bank account after selling your bitcoin, the Coinbase app makes it as easy as transferring funds from one bank to another. Similar to conventional bank transfers or ATM withdrawals, exchanges like Coinbase set a daily limit, and it may take between a few days and a week for the transaction to be completed.
The easiest way to buy bitcoin is to purchase it through an online exchange like Coinbase.
Key question
What’s the difference between Bitcoin and Blockchain?
All bitcoin transactions and public keys are recorded on a virtual ledger called the blockchain. The ledger is effectively a chronological list of transactions. This ledger is copied—exactly—across every computer that is connected to the bitcoin network, and it is constantly checked and secured using a vast amount of computing power across the globe. The blockchain concept has turned out to be powerful and adaptable, and there are now a wide variety of non-cryptocurrency-related blockchains that are used for things like supply-chain management. The ‘Bitcoin Blockchain’ specifically refers to the virtual ledger that records bitcoin transactions and private keys.
How to use Bitcoin
Back in 2013, a bitcoin enthusiast named Laszlo Hanyecz created a message-board post offering 10,000 BTC – which then was worth around $25 – to anyone who would deliver two pizzas to his Jacksonville, Florida, home. As the legend goes, those two pizzas, which another bitcoin early-adopter bought from a local Papa John’s, marked the first successful purchase of non-virtual goods using bitcoin. Thankfully it’s a lot easier to use bitcoin these days!
It’s simple: Transactions using BTC aren’t that different from those using a credit or debit card, but instead of being asked to enter card info, you’ll simply be entering the payment amount and the vendor’s public key (similar to an email address) via a wallet app. (When transacting in person using smartphones or tablets, often a QR code will pop up to simplify the process – when you scan the code, your wallet app will automatically enter the pertinent information.)
It’s private: One of the benefits of paying with bitcoin is that doing so limits the amount of personal information you need to provide. The only time you need to share your name and address is if you’re purchasing physical goods that need to be shipped.
It’s flexible: As to what you should do with your bitcoin, that depends completely on your personal interests. Here are some ideas:
You can sell it for cash using an exchange or a Bitcoin ATM.
You can spend it online or in brick-and-mortar retailers as you would any other currency by using a Bitcoin debit card.
You can hold on to some or all of it as part of your investment and savings strategy.
You might choose to that is close to your heart (check out).
And if you have a serious budget and unfulfilled astronaut dreams? Richard Branson’s Virgin Galactic happily accepts BTC in exchange for the opportunity to blast off on one of its forthcoming space-tourism missions.
Due to the cryptographic nature of the Bitcoin network, bitcoin payments are fundamentally more secure than standard debit/credit card transactions.
What makes Bitcoin a new kind of money?
Bitcoin is global. You can send it across the planet as easily as you can pay with cash in the physical world. It isn't closed on weekends, doesn’t charge you a fee to access your money, and doesn't impose any arbitrary limits.
Bitcoin is irreversible. Bitcoin is like cash, in the sense that transactions cannot be reversed by the sender. In comparison, credit cards, conventional online payment systems, and banking transactions can be reversed after the payment has been made—sometimes months after the initial transaction—due to the centralized intermediaries that complete the transactions. This creates higher fraud risk for merchants, which can lead to higher fees for using credit cards.
Bitcoin is private. When paying with bitcoin, there are no bank statements, or any need to provide unnecessary personal information to the merchant. Bitcoin transactions don’t contain any identifying information other than the bitcoin addresses and amounts involved.
Bitcoin is secure. Due to the cryptographic nature of the Bitcoin network, bitcoin payments are fundamentally more secure than standard debit/credit card transactions. When making a bitcoin payment, no sensitive information is required to be sent over the internet. There is a very low risk of your financial information being compromised, or having your identity stolen.
Bitcoin is open. Every transaction on the Bitcoin network is published publicly, without exception. This means there's no room for manipulation of transactions (save for a highly unlikely 51% attack scenario) or changing the supply of bitcoin. The software that constitutes the core of Bitcoin is free and open-source so anyone can review the code.
Bitcoin is safe. In more than ten years of existence, the bitcoin network has never been successfully hacked. And because the system is permissionless and open-sourced, countless computer scientists and cryptographers have been able to examine all aspects of the network and its security.
Where does Bitcoin come from?
Bitcoin is virtually ‘mined’ by a vast, decentralized (also referred to as ‘peer-to-peer’) network of computers that are constantly verifying and securing the accuracy of the blockchain. Every single bitcoin transaction is reflected on that ledger, with new information periodically gathered together in a “block,” which is added to all the blocks that came before.